Easy Raspberry Pi OS Install: Imager Guide & More!
Ever found yourself wrestling with the complexities of updating a Raspberry Pi remotely? Mastering remote updates and efficient administration of your Raspberry Pi devices is no longer a luxury, but a necessity for seamless operation and enhanced security.
From ensuring your IoT devices remain secure against evolving threats to streamlining updates across a fleet of devices, the ability to remotely manage your Raspberry Pi is crucial. This guide delves into the best practices, tools, and techniques to achieve just that, transforming the way you interact with these powerful little computers.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Importance of Remote Updates | Highlights the need for security patches, performance improvements, and feature enhancements that require remote updating. |
| Best Practices for Remote Updates | Details essential steps to ensure a smooth and secure remote update process. |
| Tools for Remote Updating | Explores various software solutions and methods for efficiently managing updates on Raspberry Pi devices. |
| Remote Administration Techniques | Provides tips and strategies for managing and monitoring Raspberry Pi devices remotely at scale. |
| OTA Updates for IoT Devices | Discusses the significance of Over-The-Air updates for Raspberry Pi devices in IoT applications. |
| Raspberry Pi Imager | An overview of how to use Raspberry Pi Imager for OS installation and updating. |
| SSH for Remote Access | Explains how to use SSH for secure remote access to Raspberry Pi devices. |
| Updating with APT | Instructions on how to use the APT package manager to update the OS and software packages. |
| Hardware Considerations | Notes on hardware requirements and considerations for different Raspberry Pi models. |
| Reference Website: Raspberry Pi Official Website |
To begin, consider the process of setting up your Raspberry Pi from scratch. The Raspberry Pi Imager stands out as a user-friendly tool designed for installing the Raspberry Pi OS and other operating systems onto a microSD card. This method offers a streamlined approach, ensuring your Raspberry Pi is ready for use quickly and efficiently. Simply download and install the Raspberry Pi Imager on a computer equipped with an SD card reader. Then, insert the SD card you intend to use with your Raspberry Pi into the reader.
The latest version of the Raspberry Pi Imager can be found either in APT or directly downloaded from the software page on raspberrypi.com. It's crucial to use a recent version of the Raspberry Pi OS that is compatible with your specific Raspberry Pi model. For instance, a Raspberry Pi 4 won't boot on Stretch, and a Raspberry Pi 3B+ is incompatible with Jessie. The current stable version, at the time of this writing, is Raspberry Pi OS Bullseye. If you're running an older version, it's advisable to update to ensure compatibility and access to the latest features and security enhancements.
Beyond initial setup, regular updates are essential for maintaining the health and security of your Raspberry Pi. This is where the concept of remote updating becomes invaluable. Imagine you have multiple Raspberry Pi devices deployed in various locations, perhaps as part of an IoT network. Manually updating each device would be incredibly time-consuming and impractical. Remote updating allows you to push updates to these devices from a central location, ensuring they all have the latest security patches and software improvements.
When engaging in remote updating, following best practices is paramount. A smooth and secure process hinges on several key steps. First and foremost, always ensure you have a reliable network connection. Interrupted updates can lead to corrupted files and non-bootable systems. Secondly, regularly update both the operating system and software packages. This proactive approach minimizes vulnerabilities and enhances overall performance.
- Patrick Fluegers Wife Discovering The Love Life Of The Chicago Pd Star
- Alex Landi Finding Love And Support With His Partner
Several tools are available to facilitate remote updates on Raspberry Pi, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. One of the most basic, yet powerful, tools is SSH (Secure Shell). SSH provides a secure way to access your Raspberry Pi's command line remotely. This allows you to execute update commands, transfer files, and perform other administrative tasks as if you were physically connected to the device.
For more automated and scalable solutions, consider tools designed specifically for remote updates. These tools often provide features such as scheduled updates, rollback capabilities, and centralized monitoring. Some popular options include Ansible, Chef, and Puppet. These configuration management tools allow you to define the desired state of your Raspberry Pi devices and automatically enforce those configurations across your entire fleet.
The default package manager for Raspberry Pi, APT (Advanced Package Tool), is another essential tool for remote updates. APT allows you to update packages and the operating system using simple commands. For example, the command "sudo apt update" refreshes the package lists, while "sudo apt upgrade" installs the latest versions of all installed packages. Combining APT with SSH provides a straightforward way to keep your Raspberry Pi devices up to date.
Managing remote Raspberry Pi devices at scale requires careful planning and execution. One crucial aspect is maintaining regular heartbeats. Implement SSH keepalives or MQTT pings to monitor connectivity. This ensures you're alerted if a device goes offline, allowing you to investigate and resolve the issue promptly. Another best practice is to use a centralized logging system. This allows you to collect logs from all your Raspberry Pi devices in one place, making it easier to troubleshoot issues and identify potential security threats.
Remote OTA (Over-The-Air) updates are particularly important for IoT devices based on Raspberry Pi. As IoT technology evolves, it's essential for administrators to plan for device updates. Vendors often release fixes and updates to the software, device controllers, or firmware, and administrators must be prepared to deploy these updates efficiently. The first step is to regularly check for firmware updates available for your Raspberry Pi.
To ensure optimal performance, consider the hardware requirements of your Raspberry Pi devices. While a Raspberry Pi 5 is overkill for some applications, it might be necessary for others. Similarly, a Raspberry Pi Zero W, while suitable for basic tasks, might be too slow for more demanding workloads. This guide used a Raspberry Pi 3 to download the source code, but even the most basic model should work.
When receiving a file on a Raspberry Pi from a remote device, select the file from the right column (under "remote"), then click "receive." This allows you to transfer files securely and efficiently. Additionally, you can use an iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch, or Mac to control your Homebridge accessories and set up automations. Control your devices using the app you choose, such as the Apple Home app, Eve for HomeKit, or any other third-party HomeKit apps.
For more advanced applications, consider using multiple VRXs with basic radio controls or setting up a remote server with two streaming modes across both LAN and WAN (internet). This allows you to access your Raspberry Pi from anywhere securely using a remote access solution that connects to your Raspberry Pi desktop and command line directly from any browser.
It's also possible to boot your Raspberry Pi from a USB device. The Raspberry Pi will still boot from the SD card, but only reads bootcode.bin from the SD card; the rest of your operating system resides on the USB device. This can improve performance and provide more storage space.
To connect to your Raspberry Pi remotely, enter the password when prompted. To download updates, use the following commands in the terminal: "sudo apt update" and "sudo apt upgrade." If you are working with a Raspberry Pi 400, select a Raspberry Pi 4 device. Next, click on "Choose OS," scroll to the bottom of the list, and choose "Use Custom." Browse to where you have downloaded the Parrot OS image file, select it, and click open.

Remote Into Raspberry Pi From Windows Raspberry

Mastering Remote Raspberry Pi And Iot Device Update Download On Windows
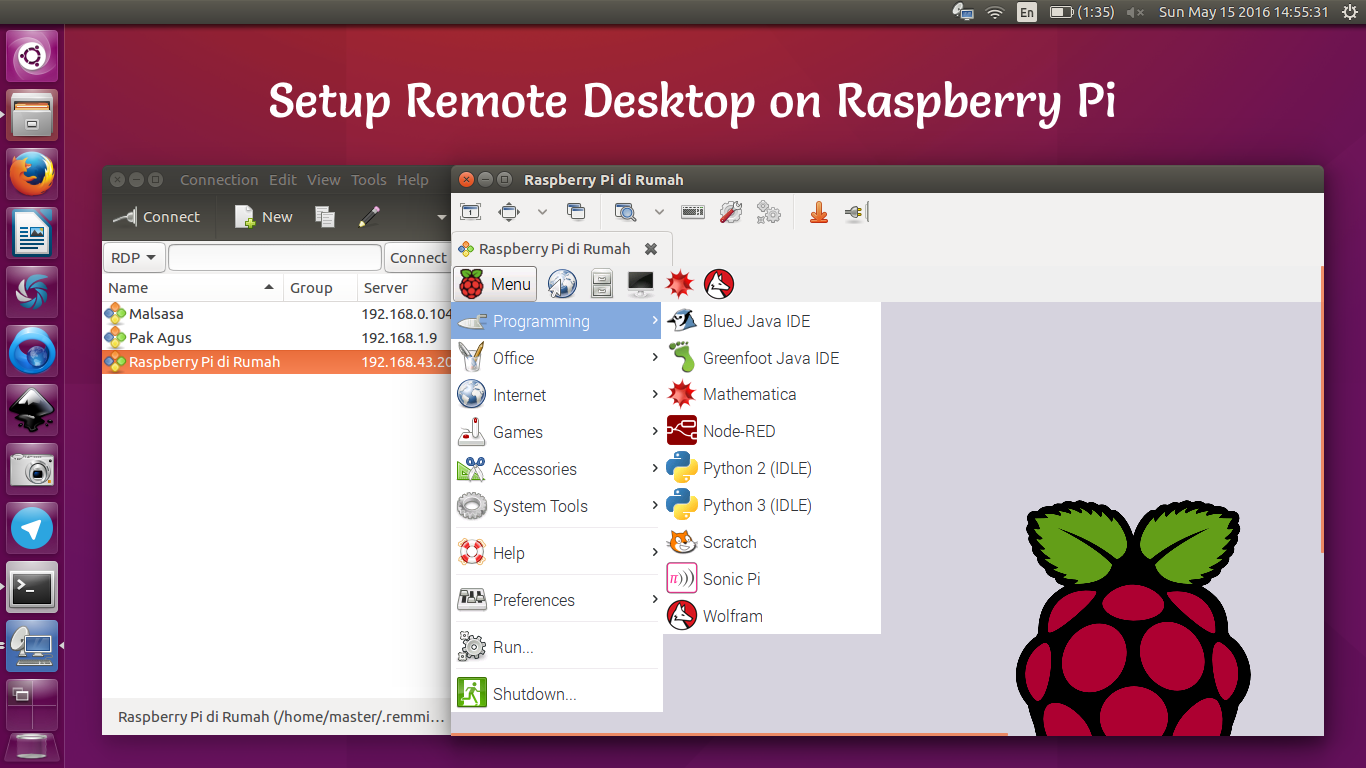
Best Remote Update Raspberry Pi Download A Beginner's Guide For Tinkerers